SSL/TLS Protocols, Communication and Data Security

Introduction
Hello everyone with a new security blog post! In our new series “Understanding SSL/TLS Fingerprints”, we will give you a detailed introduction to SSL and TLS Protocols and then we will talk about how we can use them to hunt C&C servers, which we call Command and Control. Good reading in advance.
What are SSL and TLS?
SSL and TLS are essentially internet protocols. These internet protocols secure data communication over the internet. Their main purpose is to ensure confidentiality, integrity and authentication during data transmission. Today, these protocols are mainly used for communication between web browsers and servers, and are involved in the transmission of sensitive information without it falling into the hands of third parties.
What is SSL?
SSL, also known as Secure Sockets Layer, is a protocol first developed by Netscape Communications in the mid-1990s. However, over time, this protocol evolved into a more reliable version, TLS, because it contained too many vulnerabilities. In the process of this evolution, it was standardized by the IETF while moving to TLS. SSL 3.0 is the most widely used version of this protocol, but due to its vulnerabilities, it is not preferred or recommended.
What is TLS?
TLS, also known as Transport Layer Security. It has emerged as a more secure version of SSL. TLS includes data integrity and authentication mechanisms, especially the secure transmission of data.
However, the information I want to convey to you in this series is not just explanations. We will cover the subject in detail from the beginning to the end with a plot. So let’s move on without wasting time. Next, the working principles of these protocols.
Working Principles of SSL and TLS
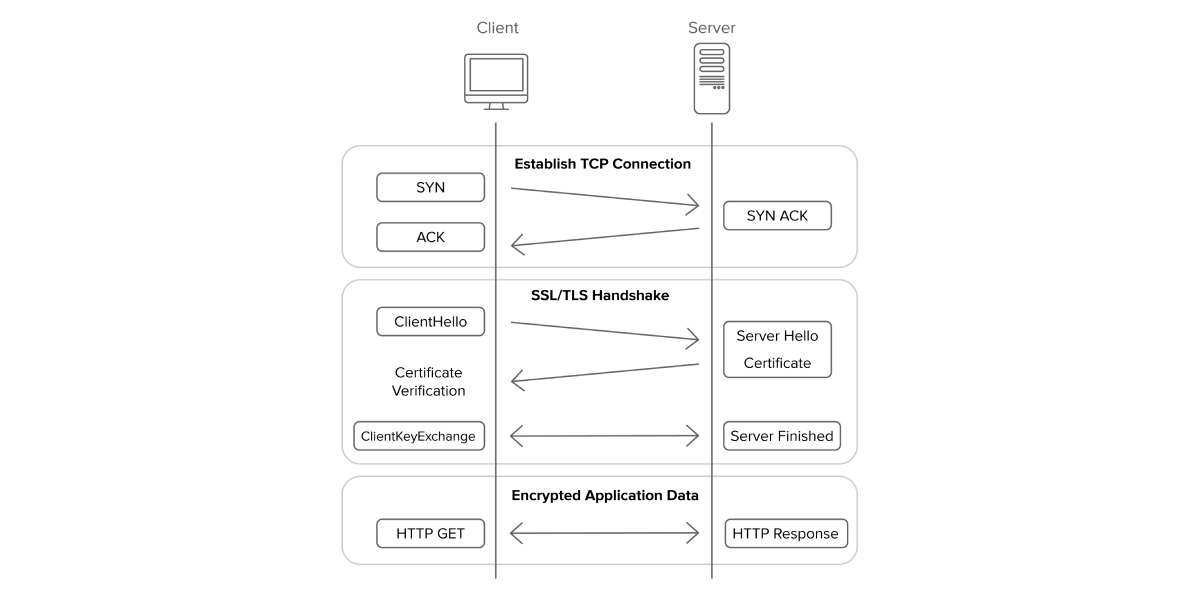
Both protocols work using a “handshake” protocol, commonly referred to as a binary handshake. This handshake event involves both parties authenticating and setting encryption parameters. I’ve mentioned it visually above, but here’s the plot with explanations:
- Start: The client requests a connection to the server it wants to connect to and declares the encryption algorithms it supports.
- Authentication: The server responds to the client and authenticates itself with a digital certificate.
- Client Key Exchange: The client generates a random symmetric key using the server’s public key and encrypts it with the server’s public key. The server decrypts this symmetric key with its private key.
- Encryption: The client and server now encrypt their communication with the symmetric key. This prevents third parties from accessing the data.
- Usage and Termination: The client and server exchange data using the secure connection and the connection is securely terminated when the communication ends.
When a connection is tried to be established between the client and the server on SSL/TLS, they can establish a connection with each other on these protocols by going through the above steps.
A Note
“Client Hello” and “Server Hello” have an important place in this blog series on the picture I have attached here to explain to you. You can even say that this is where it all started.
Basic Principles of SSL and TLS
Well, we have talked about privacy, security, authentication and so on, but now let’s see what they mean for us.
The Role of SSL and TLS in Communication Security:
Confidentiality: Confidentiality is based on encrypting and preventing access to data by third parties.
Data Integrity: Data integrity refers to the integrity of the data transmitted from the client to the server or from the server to the client. This prevents the data from being altered and ensures the security of the data.
Authentication: It is based on the server being authenticated by the client. Thus, the data between the server and the client cannot go beyond the conditions set by the server and the client.
Reliability: This item refers to the reliability of accessing the data on the internet.
Now that we have talked about communication security, let’s talk about data integrity.
The Role of SSL and TLS in Data Integrity:
SSL and TLS should naturally operate on the transmission of data in the first instance. Then it covers the integrity of the data. The reason for this is actually a cycle. There must be communication so that data can be transmitted. There must be data so that there can be communication. Both are reasons for each other’s existence. We will understand these concepts better in the rest of our article. Now let’s continue on data integrity.
Data Integrity actually tells us that the data transmitted is exactly the same as the data that is intended to be transmitted on the internet or network due to the structure of SSL / TLS and guarantees this. If we scenarioize, there are scenarios where a corporate file is changed by threat actors and attacked. For this reason, when the integrity of the data is communicated not only institutionally but also individually through these two protocols, the integrity of the data to be transmitted between the device transmitting the data and the device receiving the data is completely ensured. The data sent reaches the receiver in the same way.
Why does all this matter to us?
Actually, the goal is to prepare a complete infrastructure for the hunting of command and control servers. Of course, I realize that this is a very theoretical blog post, but too much more detail would miss our focus and distract us from our purpose.
For the first blog post of our series, we have created a nice information infrastructure on the continuation of the blog series. That’s it for now, but see you in our next blog post “SSL/TLS Fingerprints, Uses and Key Features”!